Mac OS X ipconfig
© May 2019 Anthony Lawrence
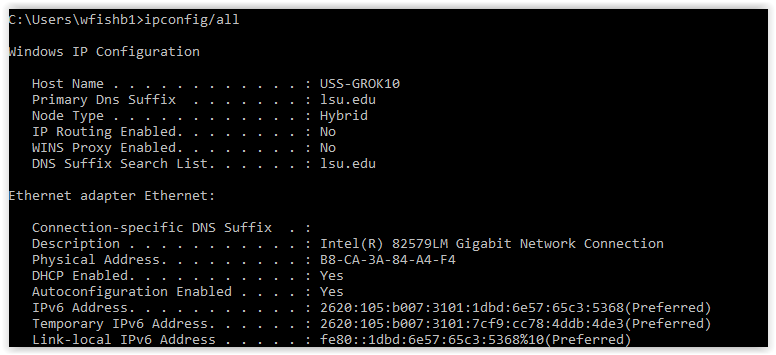
At the command prompt, type 'ipconfig /all' without quotes. (space between g and /) Alternatively, if using Windows XP, you can use the command 'getmac'. Your MAC Address is listed under 'Physical Address' as a series of 6 groups of two digits, letters and numbers, separated by dashes, such as in the image below. View All Network Setting. The “ifconfig” command with no arguments will display all the active. What is the IPCONFIG command for MAC OSX? As OSX is based on UNIX you need to type in the following command from a terminal prompt. This has been tested on: OSX Mavericks, Yosemite, EL Capitan. This command should also work for other versions of OSX. Download ipconfig GUI - Provides a user-friendly interface for the ipconfig command that is usually launched via the Windows console to see the TCP/IP, DHCP and DNS configuration. This can be used to get mac address for remote computers also. Below are few examples on how to use this command. It works on XP, Vista, Windows 7, Server 2003 and Server 2008 operating systems. Get mac addresses from CMD. Just run the command getmac to get the mac.
Ipconfig In Windows 10
July 2006

If you momentarily forget where you are at a Mac OS X terminal session, you might type 'ipconfig /all' or something equally Windowish. You will get a response:
Mac Command For Ipconfig
usage: ipconfig <command> <args>>
where <command> is one of waitall, getifaddr, ifcount, getoption, getpacket, set, setverbose
What's this? You already know you mistyped: on Mac OS X you probably meant to run 'ifconfig -a' just as you would on Linux. But 'ipconfig' is different, and is actually something good to have in your bag of tricks.
The first thing ipconfig can do for you is quickly give you all your dhcp info:
$ ipconfig getpacket en0
op = BOOTREPLY
htype = 1
flags = 0
hlen = 6
hops = 0
xid = 1045997387
secs = 0
ciaddr = 0.0.0.0
yiaddr = 192.168.9.30
siaddr = 0.0.0.0
giaddr = 0.0.0.0
chaddr = 0:16:cb:8d:38:f7
sname =
file =
options:
Options count is 7
dhcp_message_type (uint8): ACK 0x5
subnet_mask (ip): 255.255.255.0
lease_time (uint32): 0x93a80
router (ip_mult): {192.168.9.254}
domain_name_server (ip_mult): {192.168.9.254}
server_identifier (ip): 192.168.9.254
end (none):
There are shortcuts to the items listed under 'options':
$ ipconfig getoption en0 router
192.168.9.254
$ ipconfig getoption en0 domain_name_server
192.168.9.254
'ipconfig getifaddr en0' is a quick way to just get the ip address.You can also use ipconfig with its 'set' options to change an interface from DHCP to manual or vice-versa. That's temporary; it doesn't write any start up files.
If you are having difficulty with DHCP, ipconfig has one more use: you can (as root) set verbose logging with 'ipconfig setverbose 1'. With that set, you get minor debugging info written to syslog (/var/log/system.log on my system), but you also get a separate BOOTP/DHCP log in /var/log/com.apple.IPConfiguration.bootp that shows the full BOOTREQUEST/BOOTREPLY packet negotiation.
Think of ipconfig the next time you are looking for DHCP info on a Mac.
Got something to add? Send me email.
(OLDER) <- More Stuff -> (NEWER) (NEWEST)
Printer Friendly Version
-> -> Mac OS X ipconfig

Ipconfig Commands For Mac
Inexpensive and informative Apple related e-books:
Digital Sharing Crash Course
Are Your Bits Flipped?
Take Control of Automating Your Mac
Take Control of High Sierra
Take Control of Apple Mail, Third Edition
How to find internal and external IP addresses on Mac OS X and macOS?
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is assigned whenever your device connects to the Internet or a local network. The most frequent form of an IP address is four sets of digits with three digits per set. If your computer is connected to both a local network and the Internet, it will have an internal IP address signed by a local network and external IP address, which is the address of your Internet connection.
If you are setting up a network or sharing files, the IP address is required. In this article, we show a number of ways to find a Mac IP address. This guide applies to any version of Mac OS.
Table of Contents:
It is recommended to run a free scan with Malwarebytes - a tool to detect malware and fix computer errors. You will need to purchase the full version to remove infections and eliminate computer errors. Free trial available.
Find your internal IP Address through System Preferences
The first method, which will work on any operating system version, is to visit Network configuration in System Preferences. Open the Mac system preferences and locate Network, click on the network you are connected to, and below the Status line you will see your IP address.
Physical Address Ipconfig
For detailed information click Advanced and select TCP/IP tab where you will find more information about your network.
Find out your internal IP address by using Terminal
This method is easier and faster for Mac users who are familiar with a command line program called Terminal. Even if you have not used Terminal before, just follow the instructions and you will find the internal IP address. First, use spotlight by pressing Command and Spacebar and type Terminal. Then, press Return. Alternatively, you can find Terminal under the Utilities folder. Open finder, choose Applications, select Utilities, and then launch Terminal.
When Terminal has launched, type the following command: ipconfig getifaddr en0 (to find your IP address if you are connected to a wireless network) or ipconfig getifaddr en1 (if you are connected to an Ethernet). If you are using Mac OS X, the command ipconfig |grep inet displays detailed information about your computer signification in the network. The IP address is usually displayed beside last inet, however, this command does not work on macOS High Sierra.
Find your external IP address
To find your external IP address, there are two easy methods that work on all versions of the Mac operating system. First, open Google and Type IP in search. This will display your external address.
If you can browse the Internet, use the Mac command line. Launch Terminal, which is under the Utilities folder, and type: curl ifconfig.me or curl ipecho.net/plain ; echo. These commands will display your IP address in Terminal.
Windows Ipconfig
Video Showing how to find out your IP address on Mac:

